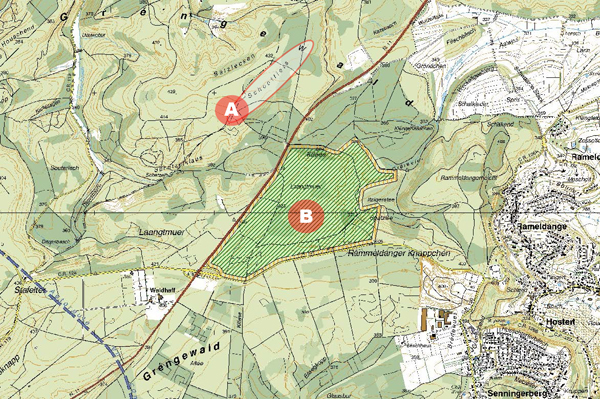
A – The “Schoeffiels” is situated 430 m above the sea level and represents the highest point of the “Gutland” part of Luxembourg.
B – The natural forest “Naturbësch”
The natural forests called “Naturbësch” are woodlands defined as a natural reserve and not designated for forestry use, in order to preserve them in their natural form.
The objectives of this procedure are following:
- Allowing the forest to develop its own ecology system and at the same time the biodiversity
- Create observation and demonstration posts in order to support forestry research
- Creation of genetic reserves and preservation of a genetic diversity
- Promote leisure and educational activities linked to this type of forest

In the natural forest reserve “Langmuer” there is no forestry management
It had been planned that up to the year 2010, 5% of the entire national woodland areas will be defined as “in free evolution”. These forests have to show a continuous area of at least 50ha and be representative for most of the upcoming forest forms.
Another condition should be that the forest is very close to an initial untouched natural status, practically without human influence and achieving the evolution criteria as age and structure of the trees, presence of deadwood and rare species.
 For those areas where the vegetation is still young and in a certain “pioneer” status, a visible mutation can be observed in lap of 5 to 10 years time. For the older forest stands, you will have to wait at least several decades before being able to see a visible alteration.
For those areas where the vegetation is still young and in a certain “pioneer” status, a visible mutation can be observed in lap of 5 to 10 years time. For the older forest stands, you will have to wait at least several decades before being able to see a visible alteration.
Analyses, observations and systematic evaluations will witness these mutations under a form of monitoring.
In order to inform and sensitize the public, the national Forest Administration previews to install informative signs and thematic educational paths in those types of areas.
The forestry reserve “Laangmuer”
The forestry reserve “Laangmuer” is extending over 103.37 ha and is all national property with the exception of 2 paths, crossing the reserve and belonging to the municipality. This reserve stands for acerbic beech groves, growing on sandstone layers. 83% of the surface is covered by Melica-Fagetum grass beech groves and only 7% by the Luzula grass beech groves. In its major part this forest is a sort of “cathedral forest” meaning that there are only high trunk trees with practically no low herb layer. It is divided into 2 distinct parts: the zone of the actual forest and the other part, a sort of buffer area forest, surrounding and protecting the inner woodland from outer influences. Because of its adjacency to Luxembourg City, this forest reserve is eminently interesting for the citizens willing to find rest in nature.
 The melica uniflora grass, typical for this kind of forest gives the name to this melica beech grove. |
 The white luzula grass is representative for the acerbic soil of the beech groves. |
 One more criteria for being classified as a natural forestry reserve is the presence of a deadwood. Numerous animal species, especially insects are able to find their habitat in deadwood.
One more criteria for being classified as a natural forestry reserve is the presence of a deadwood. Numerous animal species, especially insects are able to find their habitat in deadwood.
